What is Layer 2?
Layer 2 is the collective term for a group of blockchains and applications (like rhino.fi) built on top of the Ethereum blockchain.
These projects allows the Ethereum blockchain to scale significantly, without relying on upgrading the underlying Ethereum protocol itself.
Specifically, they allow you to exchange, transfer and invest digital assets without paying the hefty Ethereum network (gas) fees you find on layer 1, while benefiting from the security guarantees of the underlying blockchain itself. So it’s fast, safe, secure and cheap.
Why Does Ethereum Even Need Layer 2?
Ethereum is the world’s most congested blockchain.
As well as hosting its own native currency, the blockchain has pioneered the development of self-executing smart contracts which enable decentralised applications (dApps) to provide financial services without a conventional intermediary. This innovation, while revolutionary, has placed huge demand on the network and forced Ethereum to charge hefty congestion fees for a slice of its computing power.
Although the much-hyped Ethereum Merge, and its associated improvements, have made the blockchain far more efficient, it still struggles to cope with demand at peak times. So it needs a solution that will make transactions cheaper and quicker and provide the sort of experience that users are accustomed to on web2 financial apps.
Layer 2 provides a solution to these problems.
Layer 2 projects inherit the same security features as layer 1, but crucially they are free to take transactions ‘off-chain’ and execute them autonomously, free from the spacing constraints.
Indeed, whereas the main Ethereum blockchain can only process transactions individually, layer 1 scaling technology is based on the concept of rollups, whereby a project ‘rolls up’ transactions into batches, process them in bulk, then posts them back on layer 1 Ethereum for security.
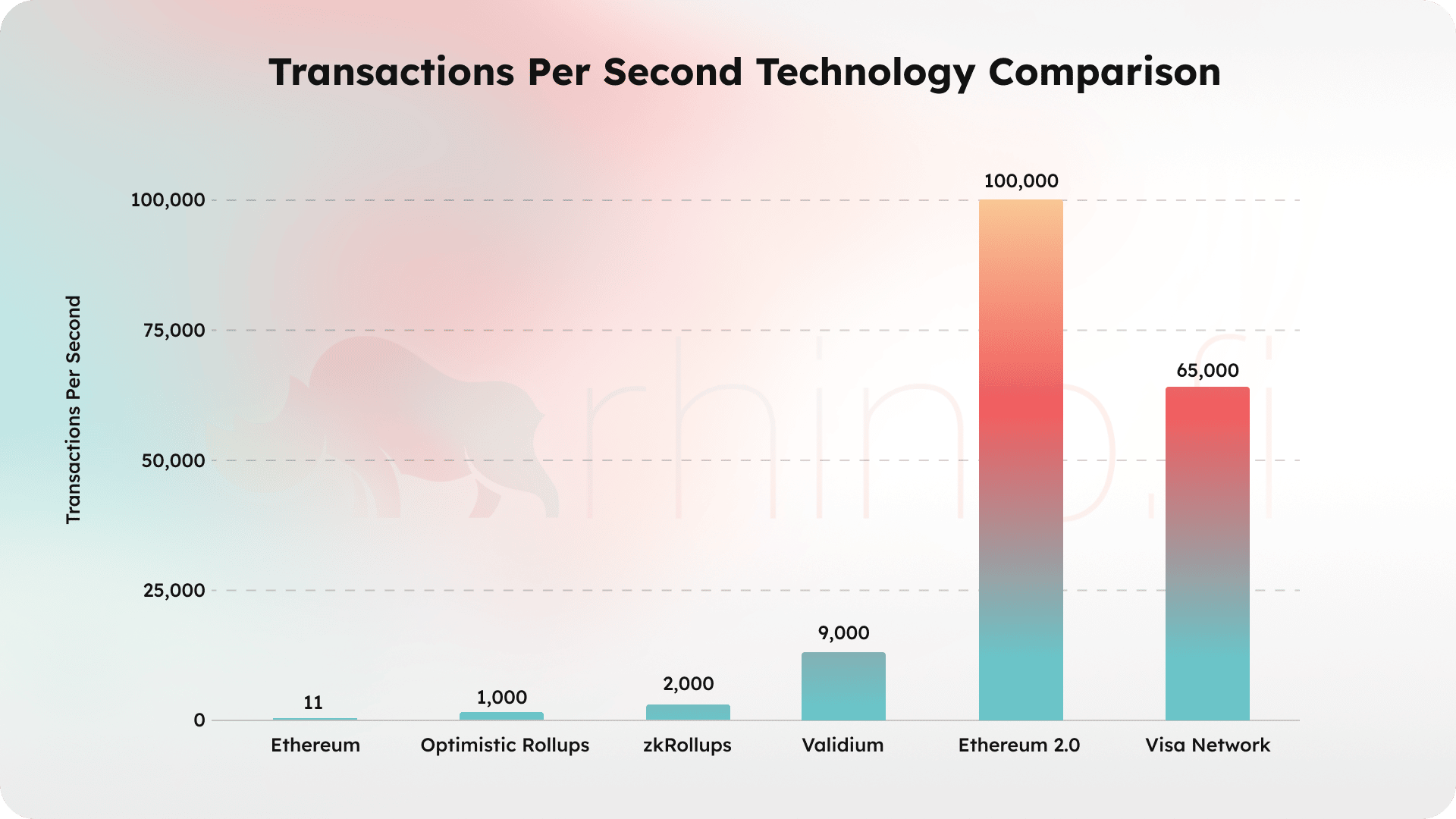
Layer 2 scaling technology comes in two forms: ZK (zero-knowledge) rollups and Optimistic Rollups.
ZK rollups use zero-knowledge cryptography, known as Snarks and Starks, to abstract transactions away from the underlying blockchain. The name ‘zero knowledge’ comes from the fact that the rollup’s validation technology uses maths to prove the legitimacy of a transaction without having to reveal sensitive details from either party.
In the case of ZK rollups, transactions are executed off-chain and then submitted to a Merkle Tree. A proof is generated periodically and submitted to a smart contract for validation. As the smart contract checks the proof, ZK rollups are known as ‘validity proof’ systems, as they minimise trust by removing the need for a third-party network of validators.
Similar to ZK rollups, Optimistic rollups abstract transactions away from the underlying Ethereum blockchain. Where they differ, however, is by relying on a network of verifiers to check each transaction for validity. All transactions are initially accepted as valid by default, but the verifiers can reject them during a subsequent challenge period.
In the case of both ZK rollup and Optimistic rollup technologies, if the operator is proven to be ‘cheating’ (either by the smart contract or the verifiers) then traders can move their assets back to the Etheruem mainchain in the last valid state – i.e. the state that was valid prior to any cheating.
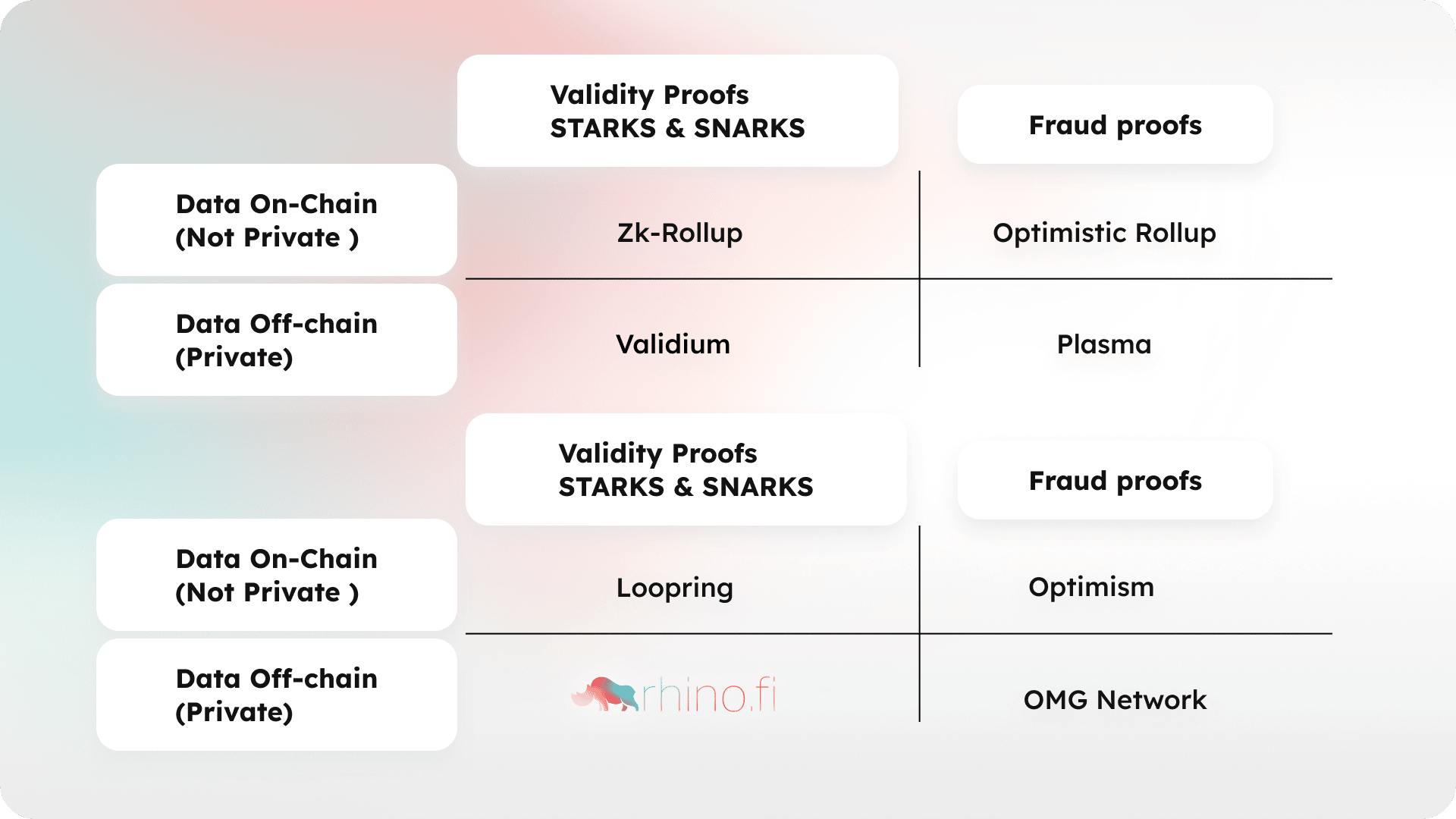
The Design Space for Layer 2 Scaling Technology
It is worth noting that the design space for layer 2 technology is nuanced. Within both ZK rollup and optimistic rollup designs, data can be held off-chain, on-chain or both, leading to varying degrees of trade-off between privacy and security.
Another key point to mention is that several types of technology purport to be Layer 2 solutions, but are in fact just separate blockchains, or side-chains. Neither of these two approaches give the strong security guarantees of the Ethereum blockchain.
What are the benefits of Layer Two trading?
1) Zero Gas Fees
You pay zero network/gas fees for each trade that you make. Saving $50 per transaction on gas fees every time you swap can add up to significant gains if you an active investor. Paying lower gas fees means greater profits in the long run.
You still pay gas fees to enter and exit the Layer 2, but these gas fees are similar to a regular smart contract interaction.
Once you have your funds within the smart contracts of an exchange such as rhino.fi, then you pay no gas fees to trade from then onwards.
2) High Speed
You can trade at high speed with an experience that is similar to that of a large centralised exchange such as Bitfinex or Binance. As well as being able to take advantage of more profit opportunities, there is also no danger of failed txs or front-running – something that plagues on-chain decentralised venues.
3) Privacy
Privacy is not a feature of all zk-rollup venues, but is a feature of some. For example, the rhino.fi decentralised exchange holds data off-chain, meaning that no one can see your trading activity or transfers, and you can operate without people stealing your alpha.
4) Instant & Cheap Transfers
Some DEXs allow private transfers between accounts. You can transfer your tokens between accounts for a few dollars instead of hundreds of dollars on-chain.
Right, so how do I trade using rhino.fi?
As we’ve mentioned, rhino.fi is an exchange built using the StarkWare ZK-rollup and Validium technology. We started out as a mere decentralised trading exchange, offering gas-free trading, privacy, deep aggregated liquidity and super fast and free transfers. Now, however, we’re a fully-fledged multi-chain DeFi aggregator, providing a gateway to hundreds of assets both same-chain and cross-chain.
With rhino.fi, you can access the whole of DeFi from a single app. We’ve abstracted away the typical problems of multi-chain, like endless network switches and annoying gas tokens, to bring the entire decentralised financial world onto layer 2.
Remember, depositing your funds to smart contracts is not the same as depositing to a centralised exchange like Binance.
As rhino.fi uses Vaildium technology, your funds are always controlled by you and can never be accessed by anyone else. This means your tokens are as secure as holding in them within a wallet on-chain. Essentially, rhino.fi gives you all the benefits of on-chain trading, but with the additional advantages of lower fees, higher speeds, privacy and deeper liquidity (better prices)
How to Make Your First Layer 2 Trade or Swap – A Walkthrough
Navigate to app.rhino.fi and connect your wallet (we support Metamask, Ledger, Coinbase Wallet and everything under the Wallet Connect banner).
Click on ‘make a deposit’ and follow the initial on-boarding two step process.
1) Enable your account. This is a one time transaction that allows you to interact with the rhino.fi smart contracts
2) Deposit tokens. Each deposit is the same as a normal smart contract interaction, but once your tokens have been deposited then you pay no fees to trade.
Swap or trade. You can use the swap tab at the top of the screen to quickly and easily swap between two tokens, or use the advanced order books trading screen.
About rhino.fi
rhino.fi is your gateway to multi-chain. Access 100s of tokens from one layer 2 wallet, all in total self-custody.
Website: https://rhino.fi/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/rhinofi
Discord: https://discord.gg/bfNDxZqPSv